|
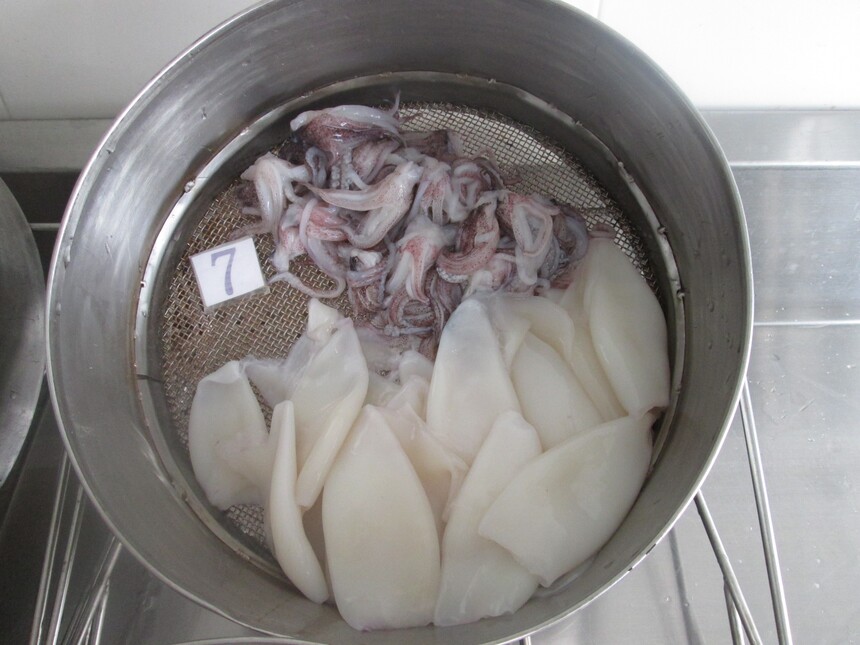
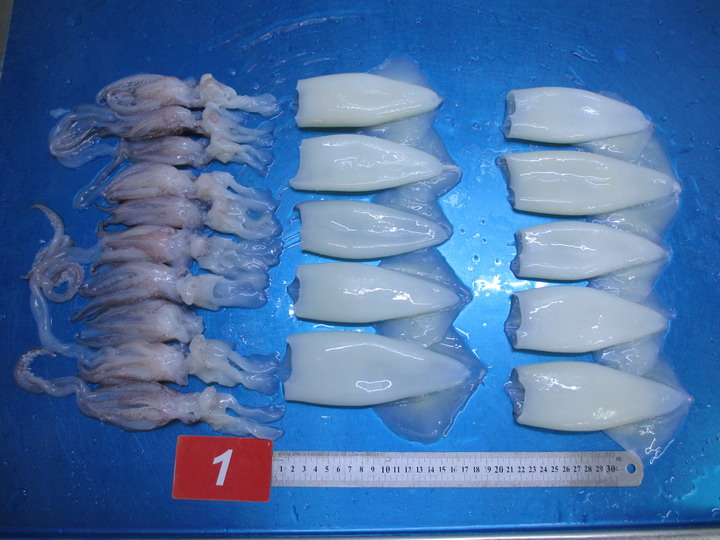
Squid tubes & tentacles(Uroteuthis Chinensis)U5Frozen squid tubes and tentacles(Uroteuthis Chinensis) Size: U5 Tubes: skinless, tip on Tentacles: eyes off, beak off, neck off, cartilage off Glazing: 0-30%glazing as per your request Packing way: BQF, 2kgs/block, 6x2kgs/carton Welcome to cooperate with us. Contact us for orders:
Blue Sea Fishery Co., Ltd. E-mail: sales@blueseafishery.cn Wechat: DORIS85789 Tel: 0086-131-5609-5220

Collect
Processing squid tubes and tentacles involves several key steps to ensure quality, safety, and suitability for consumption. Below is a detailed breakdown of the typical processing steps:
1. Raw Material Reception and Inspection
Unloading and Handling: Fresh or frozen squid (usually Loligo or Illex species) are received at the processing plant. Frozen squid is stored in cold storage (-18°C or lower) until processing, while fresh squid is kept chilled (0–4°C) to maintain freshness.
Quality Check: Inspect for freshness (e.g., firm texture, intact skin, absence of off-odors), size uniformity, and freedom from damage, parasites, or contaminants. Reject substandard squid.
2. Thawing (if frozen) Frozen squid is thawed to facilitate further processing. Common methods include:
Air Thawing: Slow thawing in a refrigerated room (4–10°C) to prevent bacterial growth. Water Thawing: Immersion in cold, potable water (≤20°C) with gentle agitation. Sometimes done in a water bath with controlled temperature to speed up thawing while maintaining quality. Vacuum Thawing: Uses low pressure to accelerate thawing, minimizing moisture loss and bacterial growth. After thawing, squid are drained to remove excess water.
3. Cleaning and Evisceration Removal of Head and Beak: Separate the head from the mantle (tube) by cutting at the base of the head. Extract the hard, parrot-like beak from the center of the tentacles.
Gut Removal: Slit the mantle lengthwise (or use a machine) to remove internal organs, including the ink sac (which can be retained for culinary use if desired), digestive tract, and gills.
Rinsing: Thoroughly rinse the tubes and tentacles with cold potable water to remove blood, debris, and residual ink.
4. Peeling (Optional but Common) Squid skin (a thin, tough membrane) is often peeled to improve texture and appearance. Methods include:
Mechanical Peeling: Machines with rotating brushes or abrasive surfaces remove the skin. Manual Peeling: Make a small incision in the skin, then peel it off by hand, starting from the mantle opening. Blanching: Brief immersion in hot water (80–90°C) loosens the skin, making peeling easier (used for larger squid).
5. Cutting and Sizing Tubes: Cut into desired forms: Tentacles: Trim the ends if necessary; larger tentacles may be cut into sections. Ensure tentacles are separated and free of small, inedible parts.
6. Blanching (Optional) Brief blanching in boiling water (1–2 minutes) sets the proteins, firms the texture, and reduces microbial load. This step is often used for pre-cooked or ready-to-eat products. After blanching, immediately cool the squid in ice water to stop cooking and preserve color.
7. Dehydration or Cooking (for Specific Products) For dried squid (a popular snack), the cleaned tubes/tentacles are seasoned (with salt, sugar, or spices) and dried in ovens or dehydrators at low temperatures (40–60°C) until moisture content is reduced to ~20–30%. For fully cooked products, squid may be grilled, fried, or boiled, then packaged as ready-to-eat items.
8. Quality Control and Sorting Inspect processed squid for defects (e.g., uneven cutting, discoloration, foreign matter). Sort by size, quality, or product type (e.g., rings vs. tentacles).
9. Packaging and Freezing Packaging: Fill cleaned, processed squid into food-grade bags, trays, or boxes. Vacuum packaging is common to extend shelf life and prevent freezer burn. Freezing: Flash-freeze (at -30°C or lower) to maintain texture and freshness. Frozen squid is typically stored at -18°C or lower for distribution.
10. Storage and Distribution Frozen squid products are stored in cold storage facilities and transported in refrigerated trucks to maintain temperature integrity until reaching retailers or consumers.
This process ensures that squid tubes and tentacles are safe, clean, and ready for various culinary applications, from seafood dishes to processed snacks. Adjustments may be made based on product specifications (e.g., fresh vs. frozen, organic vs. conventional) or regional regulations.
squid, china squid tubes and tentacles supplier, squid producer, squid exporter, squid manufacturer, seafoods supplier, squid tubes, squid rings, squid flowers
|